
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Optical Science and Engineering, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310027, China
2 Institute of Advanced Technology, Westlake Institute for Advanced Study, Westlake University, Hangzhou 310024, China
3 Hangzhou Institute for Advanced Study, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hangzhou 310024, China
Dynamical control of the constitutive properties of a light beam is important for many applications in photonics and is achieved with spatial light modulators (SLMs). Performances of the current demonstrations, such as liquid-crystal or micro-electrical mechanical SLMs, are typically limited by low (∼kHz) switching speeds. Here, we report a high-speed SLM based on the electro-optic (EO) polymer and silicon hybrid metasurface. The specially configured metasurface can not only support a high-Q resonance and large “optical–electrical” overlap factor, but also overcome the challenge of polarization dependence in traditional EO modulators. Combined with the high EO coefficient of the polymer, a 400 MHz modulation with an RF driving source of 15 dBm has been observed in the proof-of-concept device near the wavelength of 1310 nm. The device with the desired merits of high speed, high efficiency, and micrometer size may provide new opportunities for high-speed smart-pixel imaging, free-space communication, and more.
Photonics Research
2022, 10(12): 2893
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of 3D Micro/Nano Fabrication and Characterization of Zhejiang Province, School of Engineering, Westlake University, 18 Shilongshan Road, Hangzhou, 310024 Zhejiang Province, China
2 Institute of Advanced Technology, Westlake Institute for Advanced Study, 18 Shilongshan Road, Hangzhou, 310024 Zhejiang Province, China
The rocketed development concerning electro-optic polymers fundamentally motivated by its pragmatic application in envisioning second-order nonlinear optics and waveguiding are cardinal. Modern synthetic strategies consigned an outstanding optical quality amorphous polymers with enhanced properties. Documented data revealed a huge progress in understanding their implementation, however challenges still exist regarding their temporal stabilities etc. This review delivers a brief investigation of nonlinear optical (NLO) polymer materials demonstrated over previous decades. Besides, their categorical explanation along with their structural architecting via engineering polymeric backbone or functionalization of the molecular entities have been reviewed. Correspondingly, their temporal and thermal stabilities accompanied by NLO characteristics features are also discussed.
针对单核SVM分类识别SAR图像舰船目标的低精度问题, 提出了一种基于多特征提取和多核学习SVM的SAR图像舰船目标识别方法, 从特征提取和分类器训练两个方面提升目标识别的准确度。首先选用公开数据集提取舰船目标的多类特征, 然后加权融合多个核函数构造多核SVM模型, 最后使用多项特征数据训练识别舰船目标。鉴于多组目标特征存在信息冗余问题, 采用相关性系数去除某些信息高度冗余的特征, 降低特征维度。通过粒子群优化算法解决了SVM核函数的核参数选择难题。实验结果表明, 所提方法有效改善了对舰船目标的识别性能, 综合识别准确率由传统SVM的87.18%提高至92.31%。
舰船识别 多核学习 粒子群优化 特征提取 SAR Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) ship recognition Multi-Kernel Learning (MKL) Support Vector Machine (SVM) SVM Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) feature extraction
1 天津中医药大学中药学院, 天津 301617
2 天津中医药大学组分中药国家重点实验室, 天津 301617
郁金作为行气活血、通经止痛的要药,近年来受到广泛的关注。为了对四种郁金的道地性和基原进行鉴别和质量控制,采用太赫兹时域光谱技术结合化学计量法(支持向量机法、主成分分析法)对郁金的四种基原进行分类和鉴别。构建了斜坡耗损多类支持向量机(Ramp Loss K-SVC)法、随机森林(RF)法和极限学习机算法(ELM)的三种模型对四种不同基原的郁金进行区分,并开发了 Ramp Loss K-SVC方法,优化了模型参数,使四种郁金的鉴别率提高至93%。该研究为容易混淆的四种基原郁金鉴别提供一种新兴的鉴别技术。
太赫兹技术 太赫兹时域光谱 郁金 支持向量机法 鉴定 激光与光电子学进展
2021, 58(22): 2200002
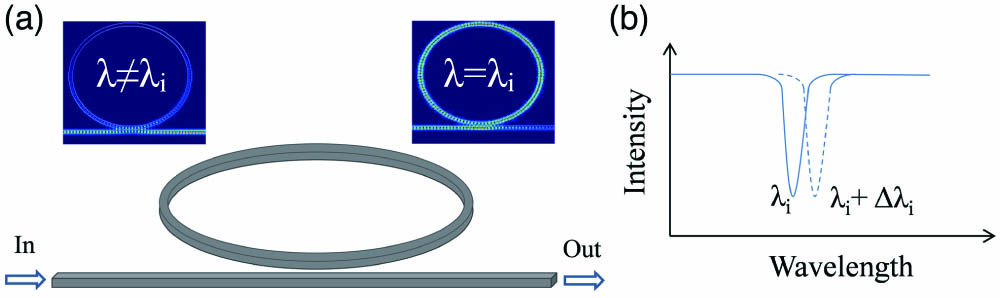
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of 3D Micro/Nano Fabrication and Characterization of Zhejiang Province, School of Engineering, Westlake University, Hangzhou 310024, China
2 Institute of Advanced Technology, Westlake Institute for Advanced Study, Hangzhou 310024, China
3 Interdisciplinary Graduate School of Engineering Sciences, Kyushu University, 6-1 Kasuga-koen, Kasuga, Fukuoka 816-8580, Japan
Electro-optic (EO) ring resonator modulators have a number of communications and scientific applications, including analog optical links, optical signal processing, and frequency comb generation. Among the EO materials used to fabricate ring modulators, the EO polymer has many promising characteristics, including a high EO coefficient of 100–200 pm/V (3–7 times larger than that of ), an ultrafast EO response time (), a low dielectric constant (3 to 4) with very little dispersion up to at least 250 GHz, and a straightforward spin-coating fabrication process. These inherent characteristics will be able to combine excellent EO properties with simple processing in achieving exceptional performance in a variety of high-speed optical modulation and sensing devices. This review focuses on the research and recent development of ring resonator modulators based on EO polymers. The first part describes the operation principle of EO ring resonator modulators, such as modulation mechanism, EO tunability, and 3 dB bandwidth. Subsequently, the emphasis is placed on the discussion of the ring modulators with EO polymers as the waveguide core and the improvement of EO modulation by using an EO polymer/titanium dioxide hybrid core. At the end, a series of EO polymers on silicon platforms including slot modulators, etching-free modulators, and athermal modulators are reviewed.
electro-optic polymer ring resonator high-bandwidth modulator Chinese Optics Letters
2021, 19(4): 041301
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Hebei Semiconductor Research Institute, Shijiazhuang 050051, China
2 National Key Laboratory of ASIC, Hebei Semiconductor Research Institute, Shijiazhuang 050051, China
3 School of Electronic and Information Engineering, Xi'an Jiaotong University, Xi'an 710049, China
In this work, we investigate the influence of defect concentration of the diamond substrates on the performance of hydrogen-terminated diamond field-effect transistors by Raman spectra, pulsed I–V characteristics analysis, and radio frequency performances measurements. It is found that a sample with higher defect concentration shows larger drain-lag effect and lower large-signal output power density. Defects in the diamond act as traps in the carrier transport and have a considerable influence on the large-signal output power density of diamond field-effect transistors. This work should be helpful for further performance improvement of the microwave power diamond devices.
Journal of Semiconductors
2020, 41(12): 122801
1 重庆大学光电技术及系统教育部重点实验室,重庆 400044
2 中国石油化工股份有限公司青岛安全工程研究院,山东 青岛 266000
分布式光纤传感系统利用光纤既能传感又能传输信号的特性实现对光纤沿线振动、应变、温度等物理量的长距离连续测量,在周界安防、电网管道监控、大型结构健康监测等领域具有十分广阔的应用前景。上述的实际应用中,事件或故障的发生通常表现为振动、应变以及温度等物理量的改变,振动的探测频响高低、应变探测的动态响应能力以及多参数的同时测量都会影响事件的定位或预警。因此,振动的宽频测量、应变的动态测量以及多参数测量,对事件定位和信息完整捕获起着至关重要的作用,能够推动分布式光纤传感的应用发展。本文介绍了近年来在分布式光纤传感系统中,基于瑞利散射的宽频振动测量、基于布里渊散射的应变动态测量以及基于多散射的多参数测量取得的研究进展。
分布式光纤传感 多参数测量 瑞利 布里渊 拉曼 distributed optical fiber sensing multi-parameter measurement Rayleigh Brillouin Raman
1 重庆大学光电技术及系统教育部重点实验室,重庆 400044
2 中国石油化工股份有限公司青岛安全工程研究院,山东 青岛 266000
光纤传感系统离不开激光光源,作为被测量信号载体的光波,激光光源本身的性能,如激光器的功率稳定性、线宽、相位噪声等参数对光纤传感系统的探测距离、探测精度、灵敏度以及噪声特性起决定性的作用,因此发展优质激光光源已成为近些年的研究热点。本文简要论述了激光光源在光纤传感领域的发展状况;重点介绍了窄线宽激光光源、可调谐激光光源以及宽带白光光源在光纤传感技术领域中的应用需求;概括了现有激光光源在光纤传感中所面临的主要限制因素和关键技术。为了进一步提高光纤传感系统的性能指标,获得可在任意波段、任意时刻实现的超窄、超稳理想激光光源将是未来光纤传感的一个主要研究方向。
光纤传感 窄线宽激光光源 可调谐激光光源 白光光源 optical fiber sensing narrow-linewidth laser source tunable laser broadband white light source
1 中国工程物理研究院 应用电子学研究所, 高功率微波技术重点实验室, 四川 绵阳 621900
2 强电磁工程与新技术国家重点实验室(华中科技大学), 武汉 430074
通过发射光谱测量和拟合不同的微波脉宽和气压下C波段微波放电的氮气等离子体振动温度、转动温度和电子激发温度。气压在266~400 Pa时, 等离子体的振动温度为(2700±100) K, 电子激发温度为(0.32 ±0.015) eV, 转动温度随脉宽增加而上升, 实验中测得的最大转动温度为370 K。偏离266~400 Pa时, 振动温度和电子激发温度同时出现了下降的趋势, 而转动温度出现了上升的趋势。这意味着电子激发温度和振动温度具有很强的关联性。
振动温度 转动温度 电子激发温度 微波脉冲放电 光谱测量 vibrational temperature rotational temperature electronic excitation temperature microwave-pulsed discharge spectrum measurement 强激光与粒子束
2014, 26(2): 023004





